|
Hauptseite - Stoffwechselübersicht - Krankheiten - Regal Medizin |
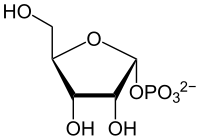
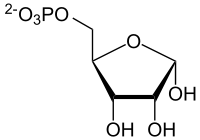
| α-D-5-Phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphat | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
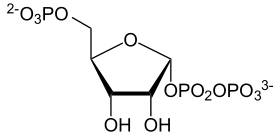 PRPP. | ||||||||||||
| Basisdaten und Verweise | ||||||||||||
|
Allgemeines
Ribose-5-phosphat, eine phosphorylierte Aldopentose, ist das Bindeglied zwischen dem HMP-Weg und der Nukleotid-Biosynthese. Es wird im HMP-Weg gebildet und wird nach Phosphorylierung zum PRPP für die Biosynthese von Purin- und Pyrimidinnukleotiden verwendet, sowie für die Bildung von Nicotinamid-adenin-dinucleotiden (NAD(P)+).
Beim Abbau der Nukleotide wird die Pentose als Ribose-1-phosphat freigesetzt und kann wieder zu Ribose-5-phosphat isomerisiert werden.
Stoffwechselwege
Freisetzung von Ribose-1-phosphat:
- Abbau der Purine
- Abbau der Pyrimidine
Biosynthese von Ribose-5-phosphat:
Verwendung von PRPP:
Bildung von PRPP aus Ribose-5-phosphat bzw. Ribose-1-phosphat
| ⇓ | Subst. | ( ⇑ ) | Co. | Enzym | EC | EG | Erkr. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||
| Phosphoglucomutase | 5.4.2.2 | Iso | ||||||||
|
||||||||||
| ATP
AMP |
Ribosephosphat- diphosphokinase | 2.7.6.1 | Tr | Gicht, PRPS- assoz. | ||||||
|
||||||||||
| Allgemeine Hintergrundfarbe für Substrate | Hintergrundfarbe Reaktionspfeile | „Schlüsselenzyme“ | |
| Energiereiche Phosphate Reduktionsäquivalente | CO2 / HCO3− C1-Reste Stickstoff |
Abk.: Tr.: Transkriptionelle Regulation, Tl.: Regulation der Translation, Lok.: Regulation über die Enzymlokalisation, Kov.: Regulation durch kovalente Modifikation, All.: Allosterische Regulation, Koop.: Kooperativer Effekt, Co.: Cofaktoren, EC: Enzymklassifikation, EG: Enzymgruppe (Oxidoreductase, Transferase, Hydrolase, Lyase, Isomerase, Ligase), Erkr.: Assoziierte Erkrankungen.
|
Hauptseite - Stoffwechselübersicht - Krankheiten - Regal Medizin |
![]()
Haben Ihnen die Informationen in diesem Kapitel nicht weitergeholfen?
Dann hinterlassen Sie doch einfach eine Mitteilung auf der Diskussionsseite und helfen Sie somit das Buch zu verbessern.