|
Hauptseite - Stoffwechselübersicht - Krankheiten - Regal Medizin |
Allgemeines
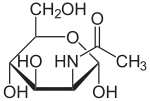
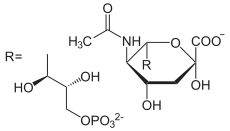
Aminozucker finden sich v.a. in Glykanen. Ihr Syntheseweg beginnt mit Fructose-6-phosphat, einem Intermediat der Glycolyse.
Übersicht über den Aminozucker-Stoffwechsel
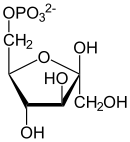
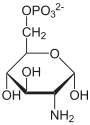
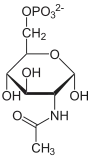
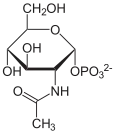
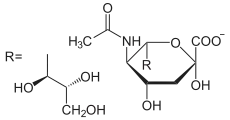
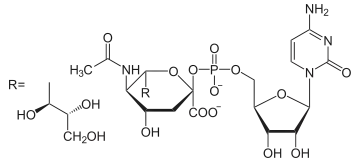
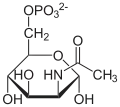
D-Fructose-6-P ⇓⇑ 2.6.1.16 / 3.5.99.6 D-Glucosamin-6-P ⇐ D-Glucosamin ⇐ D-Glucosaminid 2.7.1.1 3.2.1.- ⇓ 2.3.1.4 oder ⇓⇑ 3.5.1.25 N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamin-6-P ⇐ N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamin ( ⇐ Chitobiose ) ⇐ Chitin 2.7.1.59 3.2.1.52 3.2.1.14 ⇓⇑ 5.4.2.3 N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamin-1-P ⇓⇑ 5.1.3.8 ⇓⇑ 2.7.7.23 2.7.1.60 UDP-N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamin ⇔ N-Acetyl-D-Mannosamin ⇒ N-Acetyl-D-Mannosamin-6-P 5.1.3.14 ⇔ ⇓⇑ 5.1.3.7 ⇓⇑ 5.1.3.14 ⇓⇑ 2.5.1.56 3.1.3.- ⇓⇑ 2.5.1.56 / 2.5.1.57 UDP-N-Acetyl- UDP-N-Acetyl- N-Acetylneuraminat D-Galactosamin D-Mannosamin N-Acetylneuraminat-9-P ⇓⇑ 2.7.7.43 CMP-N-Acetylneuraminat
Einzelreaktionen
Vom D-Fructose-6-phosphat zum UDP-N-Acetyl-D-Galactosamin und -Mannosamin
| ⇓ | Subst. | ⇑ | Co. | Enzym | EC | EG | Erkr. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||
| L-Glutamin | L-Glutamin | Glutamin--Fructose-6-phosphat- Transaminase (isomerisierend) | 2.6.1.16 | Tr | |||||
|
H2O |
oder |
H2O |
oder Glucosamin-6-phosphat-Deaminase |
3.5.99.6 | Hyd | ||||
|
|||||||||
| Acetyl-CoA | Glucosamin-6-phosphat- N-Acetyltransferase | 2.3.1.4 | Tr | ||||||
|
H2O |
oder |
H2O |
oder N-Acetylglucosamin-6-phosphat- Deacetylase |
3.5.1.25 | Hyd | ||||
|
|||||||||
| Phosphoacetylglucosamin- Mutase | 5.4.2.3 | Iso | |||||||
|
|||||||||
| UTP
PPi |
UTP
PPi |
UDP-N-Acetylglucosamin- Diphosphorylase | 2.7.7.23 | Tr | |||||
|
|||||||||
| UDP-N-Acetylglucosamin- 4-Epimerase | 5.1.3.7 | Iso | |||||||
|
|||||||||
| ⇓ | Subst. | ( ⇑ ) | Co. | Enzym | EC | EG | Erkr. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||
| UDP-N-Acetylglucosamin- 2-Epimerase | 5.1.3.14 | Iso | Inclusion body- und Nonaka-Myopathie, Sialurie | ||||||
|
|||||||||
Abbau von D-Glucosaminid und D-Glucosamin
| ⇓ | Subst. | ( ⇑ ) | Co. | Enzym | EC | EG | Erkr. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||
| H2O
D-Glucosaminid |
? | 3.2.1.- | Hyd | ||||||
|
|||||||||
| ATP
ADP |
Hexokinase | 2.7.1.1 | Tr | Hämolyt. Anämie bei HK1-Def. | |||||
|
|||||||||
Abbau von Chitin und Chitobiose
| ⇓ | Subst. | ( ⇑ ) | Co. | Enzym | EC | EG | Erkr. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||
|
m H2O n N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamin, Chitin |
Chitinase | 3.2.1.14 | Hyd | ||||||
|
|||||||||
| H2O
N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamin |
β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase | 3.2.1.52 | Hyd | GM2-Gangliosidose I (Tay-Sachs), II (Sandhoff) | |||||
|
|||||||||
| ATP
ADP |
N-Acetylglucosamine-Kinase | 2.7.1.59 | Tr | ||||||
|
|||||||||
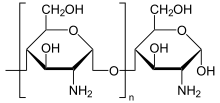
Chitin findet man in der Zellwand von Pilzen und im Außenskelett von Arthropoden, wo es für dessen Flexibilität verantwortlich ist. Strukturell entspricht es der pflanzlichen Zellulose (β-1,4-Bindungen), wobei statt D-Glucose das N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamin verwendet wird.
Biosynthese / Abbau von CMP-N-Acetylneuraminat
| ⇓ | Subst. | ⇑ | Co. | Enzym | EC | EG | Erkr. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||
| H2O
UDP |
H2O
UDP |
UDP-N-Acetyl- glucosamin- 2-Epimerase | 5.1.3.14 | Iso | Inclusion body- und Nonaka- Myopathie, Sialurie | ||||
|
|||||||||
| H2O, PEP
Pi |
PEP, H2O
PPi |
N-Acetylneuraminat- Synthase | 2.5.1.56 | Tr | |||||
|
|||||||||
| CTP
PPi |
CTP
PPi |
N-Acylneuraminat- Cytidylyltransferase | 2.7.7.43 | Tr | |||||
|
|||||||||
Biosynthese und Abbau von N-Acetylneuraminat-9-phosphat
| ⇓ | Subst. | ⇑ | Co. | Enzym | EC | EG | Erkr. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||
| ATP
ADP |
N-Acylmannosamin-Kinase | 2.7.1.60 | Tr | Inclusion body- und Nonaka- Myopathie, Sialurie | |||||
|
H2O |
oder |
H2O |
oder ? |
3.1.3.- | Hyd | ||||
|
|||||||||
| H2O, PEP
Pi |
PEP, H2O
PPi |
N-Acetylneuraminat-Synthase | 2.5.1.56 | Tr | |||||
| N-Acetylneuraminat-9-phosphat-Synthase | 2.5.1.57 | Tr | |||||||
|
|||||||||
N-Acetyl-D-Mannosamin kann zu N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamin isomerisiert werden
| ⇓ | Subst. | ⇑ | Co. | Enzym | EC | EG | Erkr. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||
| ATP | N-Acylglucosamin-2-Epimerase | 5.1.3.8 | Iso | ||||||
|
|||||||||
Allgemeines
Aminozucker werden aus D-Fructose-6-phosphat gebildet. Aminozucker gehen nach Aktivierung durch CTP oder UTP beim Menschen in den Heteroglycan-Stoffwechsel ein, z.B. in die Synthese des Saccharid-Anteils von Glycolipiden, Glycoproteinen und Proteoglykanen (Glycosaminoglycane). Bsp.:
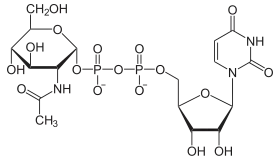
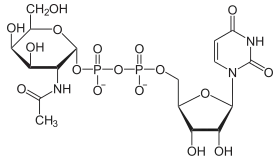
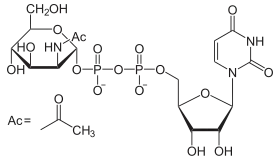
- UDP-N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamin - Synthese von Heparansulfat und GPI-Ankern
- UDP-N-Acetyl-D-Galactosamin - Synthese von Chondroitinsulfat.
- CMP-N-Acetylneuraminat (NANA) - Biosynthese der Lewis-Antigene Sialyl-Lea (Lacto-Serie) und Sialyl-Lex (Neo-Lacto-Serie), zu denen beispielsweise die Blutgruppen-Antigene des AB0-Systems gehören. NANA findet sich auch häufig am Ende der Oligosaccharidkette von Glykoproteinen z.B. von Plasmaproteinen, deren Abbau dadurch verhindert wird. NANA kann von Neuraminidasen abgespalten werden.
Weitere Funktionen:
- N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamin (GlcNAc) - Kovalente Modifikation von Proteinen an Serin- und Threonin-Resten durch die N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamin-Transferase.
Weblinks
| Allgemeine Hintergrundfarbe für Substrate | Hintergrundfarbe Reaktionspfeile | „Schlüsselenzyme“ | |
| Energiereiche Phosphate Reduktionsäquivalente | CO2 / HCO3− C1-Reste Stickstoff |
Abk.: Tr.: Transkriptionelle Regulation, Tl.: Regulation der Translation, Lok.: Regulation über die Enzymlokalisation, Kov.: Regulation durch kovalente Modifikation, All.: Allosterische Regulation, Koop.: Kooperativer Effekt, Co.: Cofaktoren, EC: Enzymklassifikation, EG: Enzymgruppe (Oxidoreductase, Transferase, Hydrolase, Lyase, Isomerase, Ligase), Erkr.: Assoziierte Erkrankungen.
|
Hauptseite - Stoffwechselübersicht - Krankheiten - Regal Medizin |
![]()
Haben Ihnen die Informationen in diesem Kapitel nicht weitergeholfen?
Dann hinterlassen Sie doch einfach eine Mitteilung auf der Diskussionsseite und helfen Sie somit das Buch zu verbessern.